Think Housing is Your Biggest Expense? Think Again!
Oftentimes people assume that housing is our single biggest expense, and although that was true in 1961, times have changed! According to research done by the Fraser Institute, last year the average Canadian family spent more on taxes than housing, food, and clothing combined. Here is the news release from the Fraser Institute along with a copy of the report.
Now although I might not be able to help you reduce the amount of taxes you pay, if you would like to review your mortgage to see if you can save any money there, please don’t hesitate to contact me anytime!
NEWS RELEASE
Taxes—not housing and basic necessities—are largest Canadian household expense.
Despite high housing costs across the country, the average Canadian family spent more on taxes in 2016 than housing, food and clothing combined, finds a new study released today by the Fraser Institute, an independent, non-partisan Canadian public policy think-tank.
“Many Canadians may think housing is their biggest household expense, but in fact the average Canadian family spent more on taxes last year than on life’s basic necessities—including housing,” said Charles Lammam, director of fiscal studies at the Fraser Institute and co-author of the Canadian Consumer Tax Index, which tracked the total tax bill of the average Canadian family from 1961 to 2016.
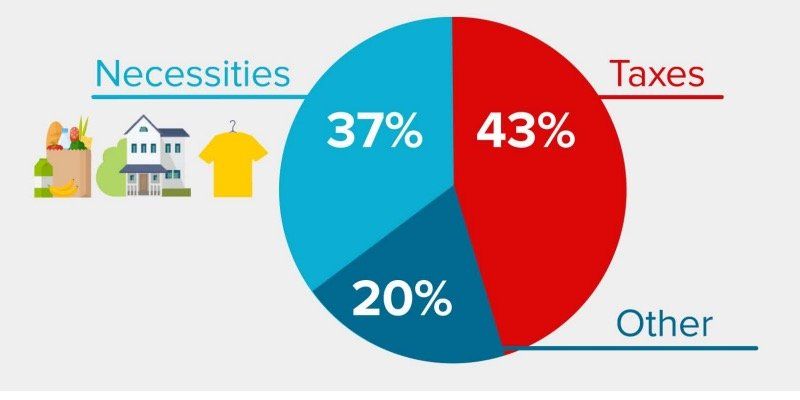
Last year, the average Canadian family earned $83,105 and paid $35,283 in total taxes compared to $31,069 on housing (including rent and mortgage payments), food and clothing combined.
In fact, the average Canadian family paid nearly twice as much of their income in taxes (42.5 per cent) as they did for housing (22.1 per cent). The basic necessities of life, which include food, clothing and housing, amounted to just 37.4 per cent of income—still less than the percentage of income going to taxes.
This represents a marked shift since 1961, when the average Canadian family spent much less on taxes (33.5 per cent) than on food, clothing and housing (56.5 per cent).
The total tax bill reflects both visible and hidden taxes that families pay to the federal, provincial and local governments including income, payroll, sales, property, carbon, health, fuel and alcohol taxes and more.
Since 1961, the average Canadian family’s total tax bill has increased by a staggering 2,006 per cent, dwarfing increases in annual housing costs (1,527 per cent), clothing (677 per cent), and food (639 per cent).
Even after accounting for inflation, the tax bill has still increased 157.6 per cent over this period.
“Taxes help fund important public services that Canadians rely on, but the issue is the amount of taxes governments take compared to what Canadians get in return,” Lammam said.
“With more than 42 per cent of their income going to taxes, Canadians might ask whether they’re getting good value for their tax dollars.”
Share
Recent Posts